BETA-LACTAMASE Hazra Database
CepA Beta-Lactamase Database
A database offering multi-level data for CepA Beta-Lactamase enzyme hosted by Hazra Lab
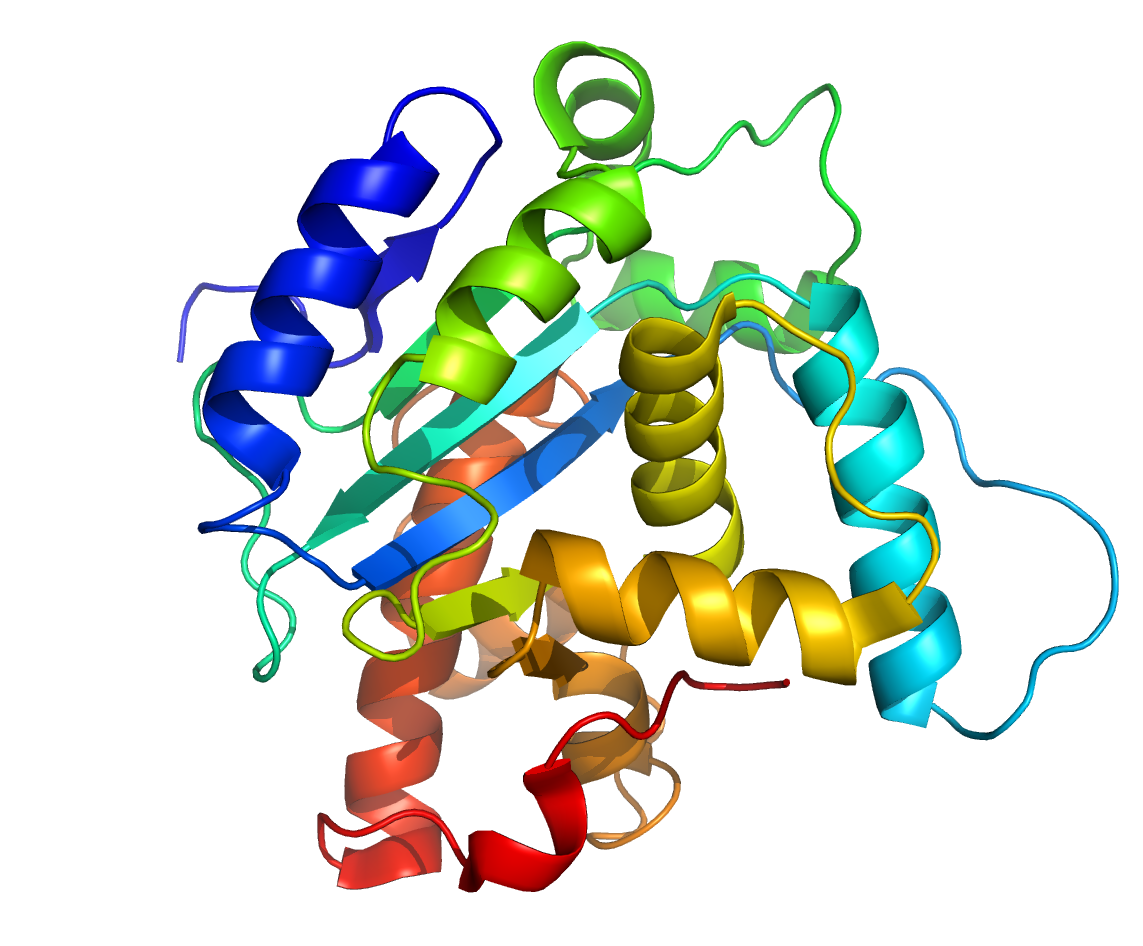
CepA is a chromosomal class A Beta-lactamase produced by the Enterobacteria Bacteroides fragilis, with a wider substrate hydrolysis profile. CepA is coded by the cepA gene and has a protein length of 272 amino acids. Based on the classification by Ambler, cepA shows the four conserved elements of class A beta-lactamases. Until now, 22 allelic variants of the CepA enzyme have been sequenced. CepA shows efficient hydrolysis of cephalosporins. Bacteroides is resistant to benzylpenicillin and cephalosporidine. It is inhibited by Clavulanic acid and tazobactam but not by aztreonam. (check) but a-methoxyl cephamycins such as cefoxitin and the carbapenems have been highly active against Bacteroides species. Extended spectrum Beta lactamase (ESBL) hydrolyses cephalosporins.